The enterprise automation sector is shifting rapidly as organizations move toward 2026. We are observing a transition from scripted chatbots to Agentic AI—systems capable of reasoning, adapting, and acting independently to solve complex problems. While the market offers numerous solutions, Cognigy and Kore.ai have established themselves as major players, each bringing distinct philosophies to large-scale deployment.
Selecting the right platform requires a clear understanding of how these tools handle infrastructure, scalability, and integration. Cognigy focuses on mastering the contact center environment through deep specialization, while Kore.ai offers a unified platform designed to automate workflows across IT, HR, and customer service simultaneously.
Quick Comparison
Cognigy = Contact center specialist, excels at high-volume voice automation, ~500ms latency, low-code ease
Kore.ai = Enterprise-wide orchestrator, multi-agent workflows, knowledge graphs, ~800-1000ms latency, steeper learning curve
Best for Cognigy: B2C customer service, voice-heavy operations, quick deployment needs
Best for Kore.ai: B2B/B2E automation, cross-department processes, regulated industries, complex integrations
Cognigy.AI: The Contact Center Specialist
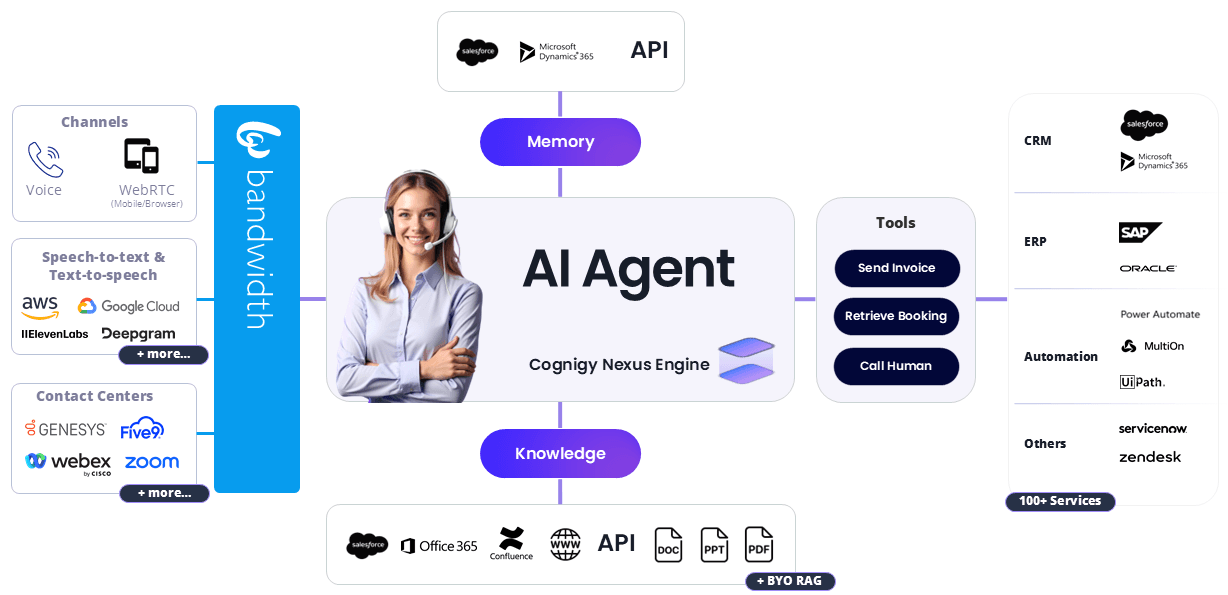
Cognigy has positioned itself as a full-stack AI platform specifically engineered for high-volume customer service operations. Its primary strength lies in its ability to manage multimodal interactions—voice, chat, and digital—at an enterprise scale. The platform currently powers over one billion annual interactions for global giants like Lufthansa and Mercedes-Benz, handling up to 25,000 concurrent sessions without performance degradation.
Recent developments have solidified its standing in the market. In July 2025, NICE acquired Cognigy for approximately $955 million, a move that accelerates its integration into broader Customer Experience (CX) ecosystems. This acquisition underscores Cognigy's focus on autonomous agents that use generative capabilities and real-time memory to resolve issues rather than simply deflecting them.
The platform relies on a specific set of architectural pillars to deliver these results. The following components form the technical basis of the Cognigy.AI infrastructure:
- Nexus Engine: This is the orchestration layer that combines Large Language Models (LLMs) with strict governance. It manages context, optimizes workflows for task decomposition, and ensures responses remain empathetic and accurate.
- AI Agent Studio: A low-code visual builder that allows teams to co-create agents. It features AI-assisted design and real-time collaboration tools, enabling faster deployment cycles for non-technical staff.
- Knowledge AI: This system uses vector-based ingestion to pull information from enterprise sources like SharePoint or Confluence. It utilizes Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide natural language answers grounded in company data.
- Enterprise Analytics: The platform includes dashboards that track millions of data points in real-time. Users can monitor journey insights and ROI metrics, such as cost savings, and export this data directly to PowerBI.
Kore.ai: The Unified Automation Platform
Kore.ai takes a wider approach, positioning itself as a comprehensive operating system for enterprise AI. Rather than focusing solely on the contact center, Kore.ai aims to orchestrate multi-agent systems that handle work, service, and process automation across an entire organization. This broad scope allows it to serve heavily regulated sectors, including banking, healthcare, and telecom, where it integrates with complex back-end systems.
The platform is recognized for its "build once, deploy anywhere" philosophy, supporting over 100 languages and 35 distinct channels. Kore.ai emphasizes the coordination of multiple specialized agents that can communicate with one another to complete end-to-end workflows. For example, a customer service agent can hand off a request to an IT automation agent without human intervention.
Kore.ai structures its capabilities around several distinct, powerful layers. The platform delivers its functionality through these core modules:
- XO Platform (v11): A unified no-code builder that manages conversational flows and generative AI integration. It serves as the primary interface for designing interactions and connecting to contact center infrastructure.
- Agent Platform: This orchestration engine manages autonomous agents and facilitates "Agent-to-Agent" (A2A) protocols. It maintains persistent memory and supports real-time streaming for both voice and digital channels.
- GALE (Generative AI Layer for Enterprises): A dedicated framework for integrating and managing LLMs. It provides prompt management, model evaluation, and security controls to ensure generative outputs meet enterprise standards.
- Security and Compliance: The platform maintains rigorous standards, including SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and GDPR compliance. It includes built-in safety controls for PII anonymization and comprehensive audit logs for all agent decisions.
Comparative Analysis: Core Capabilities and Architecture
Choosing between Cognigy and Kore.ai often comes down to how their underlying architectures handle data, reasoning, and system connectivity. While both platforms utilize Generative AI to drive automation, they apply these technologies differently to solve enterprise problems. Cognigy leans heavily into "Hybrid AI" to maintain strict control over customer interactions, whereas Kore.ai focuses on a "Multi-Agent" structure to manage broader organizational workflows.
AI Capabilities and Reasoning Engines
The intelligence layer determines how well an agent understands context, retains information, and executes tasks. Cognigy employs a strategy called "Hybrid AI," which fuses traditional NLU (Natural Language Understanding) with Large Language Models. This combination allows the system to extract precise data from complex sentences—such as identifying distinct passengers in a phrase like "me, my wife, and kids"—while still using Generative AI for fluid conversation.
Kore.ai, conversely, builds its logic around "DialogGPT" and a multi-agent orchestration framework. This setup involves supervisor agents that delegate tasks to specialized sub-agents, capable of maintaining long-term memory across different sessions.
Here is how the AI capabilities differentiate in practice:
- Cognigy Agentic AI: Focuses on LLM-powered reasoning with specific tools for multi-turn conversations. It prioritizes maintaining the "state" of a conversation even when a user jumps between topics, using "Targeted Knowledge Retrieval" to pull precise answers from documents.
- Kore.ai Multi-Agent Orchestration: Utilizes A2A (Agent-to-Agent) protocols that allow different bots to collaborate. A user might start a chat with a service bot, which then silently polls a finance bot for billing data without the user realizing a handoff occurred.
- Knowledge Handling: Cognigy uses RAG specifically optimized for enterprise sources like wikis, while Kore.ai employs advanced semantic search and knowledge graphs to support multi-turn reasoning and decision-making.
Integration Ecosystems and Connectivity
Integration capabilities define how quickly an AI platform can become useful within an existing IT stack. Cognigy’s integration strategy is intensely focused on the Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS) ecosystem. It provides deep, native connections to major telephony and support platforms, ensuring that voice and chat data flow smoothly between the AI and human agents.
Kore.ai casts a wider net, targeting back-office functions alongside customer service. Its integration library reflects a goal to automate internal employee processes just as much as external customer queries, connecting readily with ERPs and HR systems.
The following points highlight the divergent integration strategies:
- Cognigy Connectivity: Features over 100 prebuilt connectors with a strong emphasis on omnichannel support (web, phone, messaging). It integrates natively with platforms like NICE CXone, Genesys Cloud CX, and Salesforce, and offers provider-agnostic voice support (Google, Deepgram).
- Kore.ai Connectivity: Offers 75+ prebuilt integrations that span heavy enterprise systems like SAP Cloud ERP, Epic, and Microsoft Teams. It also includes over 60 ingestion connectors for unstructured data sources such as Google Drive and web crawling services.
- Extensibility: Cognigy provides an extension marketplace to embed tools directly into agent desktops, while Kore.ai offers SDKs in JavaScript and Python for building custom tools and complex backend logic.
Deployment, Latency, and Scalability
Performance metrics such as latency and deployment flexibility are major factors for technical teams. Cognigy is often favored in high-velocity voice environments because of its architecture, which minimizes delay. The platform optimizes its Voice Gateway to achieve low latency, averaging around 500ms, which is vital for preventing awkward pauses during phone conversations.
Kore.ai supports a highly structured deployment environment suited for IT-heavy organizations. It emphasizes "Lifecycle Management" with built-in CI/CD pipelines, allowing teams to move agents through development, testing (QA/UAT), and production stages systematically.
These operational differences impact how teams build and release their agents:
- Cognigy Deployment: Centers on a low-code/no-code "AI Agent Studio" that supports visual flow editing and real-time collaboration. It is designed to handle massive spikes in traffic, supporting enterprise-grade scaling up to 25,000 concurrent sessions.
- Kore.ai Deployment: Offers a mix of no-code flow builders and pro-code capabilities. It supports multi-stage release pipelines standard in software development, with an average latency of 800-1000ms, which is acceptable for chat but requires optimization for real-time voice.
- Environment Flexibility: Both platforms support cloud, on-premise, and hybrid setups. However, Kore.ai places a specific emphasis on "GALE" to manage prompt engineering and model selection securely across these environments.
Innovation Cycles and Governance: 2025 and Beyond
The rapid evolution of Generative AI has forced both platforms to accelerate their development cycles, resulting in major updates throughout 2025. Enterprises now demand systems that not only generate answers but also adhere to strict compliance standards and execute complex actions autonomously. Both vendors have responded by refining their architectures to balance the creative power of LLMs with the rigidity required for business operations.
Recent Platform Enhancements (2025)
Cognigy and Kore.ai have released updates focused on improving accuracy, reducing hallucination, and streamlining the builder experience. Cognigy’s recent releases emphasize precision in data retrieval and team collaboration, while Kore.ai has overhauled its orchestration engine to better support autonomous agents.
Cognigy.AI focused its late 2025 efforts on tightening the connection between AI agents and enterprise data. The platform introduced specific features to address the "black box" nature of generative responses:
- Targeted Knowledge Retrieval (Nov 2025): This feature allows AI Agents to access specific segments of enterprise data rather than scanning entire databases. It reduces processing overhead and increases the relevance of answers generated from internal documents.
- Collaborative Flow Editing: Recognizing that large teams build complex bots, Cognigy added real-time multi-user editing capabilities. This allows developers and conversation designers to work on the same flow simultaneously without version conflicts.
- Ops Center Improvements: New filtering options in the Operations Center provide granular control over component-specific settings, giving technical teams better visibility into system performance.
Kore.ai launched its "XO v11" platform, representing a shift toward fully autonomous orchestration. Their 2025 updates prioritize the "Agentic" model, where the system determines the best path to a solution without hard-coded decision trees:
- DialogGPT Orchestration: This engine enables autonomous topic handling, allowing the system to switch contexts fluidly. It reduces the need for manual flow design by using LLMs to determine user intent and the appropriate subsequent action.
- Advanced RAG & Agent Node v2: The update introduced a hybrid RAG approach that claims 20-30% accuracy gains. The new Agent Node supports more complex tool calling, enabling the bot to execute multi-step tasks across different backend systems.
- Unified Flow Builder: Kore.ai merged its voice and digital design environments. This allows developers to create a single logic flow that adapts automatically to the channel, whether it is an email thread or a voice call.
Governance, Security, and AI Safety
As AI agents take on more responsibility, the mechanisms for controlling them become as important as the intelligence itself. Organizations in finance, healthcare, and government cannot rely on probabilistic models alone; they require deterministic guardrails. Both platforms have built extensive governance layers, but they structure these protections differently.
Cognigy integrates governance directly into its "Hybrid AI" model. The platform allows designers to toggle between generative freedom and strict rule-based logic depending on the sensitivity of the task:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granular permission settings ensure that only authorized personnel can modify specific agent behaviors or access sensitive logs.
- Privacy and Compliance: The architecture supports GDPR and HIPAA requirements by design. It includes tools for scrubbing PII (Personally Identifiable Information) before data ever reaches an LLM.
- Trust and Safety Layers: Users can define specific boundaries for the AI. If an agent encounters a topic outside its approved scope, the system reverts to pre-defined, safe responses rather than improvising.
Kore.ai addresses safety through its dedicated "GALE" framework and a suite of "AI Safety" controls. This approach separates the management of the language model from the application logic, creating a firewall between the AI's reasoning and the enterprise's standards:
- Guardrails and Content Filtering: The platform includes configurable filters that monitor inputs and outputs in real-time. These guardrails prevent the model from generating toxic, biased, or non-compliant content.
- Evaluation Frameworks: Kore.ai provides tools for both automated and human scoring of agent performance. Teams can trace the logic behind every AI decision to audit why a specific answer was given.
- Pii Anonymization: Similar to Cognigy, Kore.ai offers automated redaction of sensitive data. This ensures that customer details remain secure even when interacting with third-party LLMs.
2026 Strategic Outlook
Looking ahead to 2026, the paths of these two platforms diverge largely due to market positioning and recent corporate shifts. The strategies reveal how each vendor plans to capture the growing budget allocations for enterprise AI.
Cognigy is set to become a core component of the NICE ecosystem following its acquisition. The 2026 roadmap focuses on the "AI Workforce," aiming to integrate Cognigy’s agentic capabilities into the NICE CXone Mpower suite. This move suggests a future where Cognigy serves as the intelligence engine for global contact centers, heavily integrated with human agent tools. The projection of 80% ARR growth indicates a focus on rapid deployment in regulated sectors, leveraging NICE’s existing dominance in the CCaaS space to scale "Human-AI" hybrid teams.
Kore.ai remains focused on broad, cross-functional automation. Their outlook for 2026 prioritizes Agentic Scaling and the concept of voice as the "digital front door." They forecast that 10% of all interactions will be fully automated by voice in the coming year. Their strategy relies on deep partnerships with major cloud providers like Microsoft and AWS to support global expansions. Kore.ai aims to capture the market of organizations that prefer a "build-vs-buy" hybrid approach, offering the infrastructure for enterprises to build their own custom agent meshes rather than just buying a pre-made support bot.
Strengths, Weaknesses, and Enterprise Fit
Selecting an AI platform requires an objective look at where each system succeeds and where it encounters limitations. While marketing materials often highlight similar features, real-world deployment reveals distinct functional differences. Cognigy and Kore.ai have carved out specific territories where they outperform the competition, driven by their underlying architectural choices.
Cognigy.AI: The CX Performance Leader
Cognigy demonstrates its highest value in high-pressure, customer-facing environments. Its architecture is engineered to handle massive spikes in traffic without failing, making it the preferred choice for industries with volatile demand, such as airlines and logistics.
Primary Strengths:
- Contact Center Autonomy: The platform excels at managing high-volume external interactions. Large enterprises like Lufthansa utilize Cognigy to automate millions of transactions, ranging from flight rebooking to refund processing, with high reliability.
- Low-Latency Voice: Cognigy maintains a technical edge in voice automation. The Voice Gateway operates with an average latency of approximately 500ms. This speed creates a natural conversational rhythm that is difficult for other platforms to match in real-time phone scenarios.
- Hybrid Control: For industries requiring strict compliance, such as automotive and insurance, the ability to switch between Generative AI and deterministic (rule-based) flows provides necessary safety. This ensures that legal disclaimers or safety warnings are delivered exactly as written.
Notable Limitations:
- Scope Limitation: The platform focuses intensely on Customer Experience (CX). While it can handle internal queries, it is less specialized for complex back-office IT or HR process automation compared to Kore.ai.
- Pro-Code Extensibility: While the low-code environment is strong, development teams looking for deep, code-heavy customization or complex custom scripting may find the environment more restrictive than open development frameworks.
Kore.ai: The Organizational Orchestrator
Kore.ai serves a different set of priorities. Its strength lies in its breadth. It connects disparate business units, allowing a large organization to build a "mesh" of agents that serve employees and customers alike. It is particularly strong in sectors like banking and healthcare, where data must flow securely between legacy systems and modern interfaces.
Primary Strengths:
- Multi-Agent Ecosystem: Kore.ai is highly effective at internal process automation. It allows for the creation of distinct agents for HR, IT, and Finance that collaborate. An employee can request time off, and the system can automatically check leave balances and update payroll without the user switching interfaces.
- Knowledge Graph Maturity: The platform utilizes advanced knowledge graphs alongside RAG. This allows for deep semantic understanding, enabling the system to reason through complex queries that require connecting facts from different documents.
- Regulatory Compliance: With certifications including SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, Kore.ai is ready for heavily regulated industries. Its PII anonymization and audit trails are extensive, meeting the requirements of global financial institutions.
Notable Limitations:
- Complexity: The depth of the platform comes with a cost. New users often find the interface and the sheer number of features substantial. It requires a longer training period for teams to become proficient compared to simpler tools.
- Voice Latency: While capable of voice interactions, average latency sits between 800-1000ms. This is adequate for many use cases but falls short of the near-instant response times required for highly sensitive voice applications.
- Entry Barrier: The platform is positioned for mega-enterprises. The pricing structure and implementation scale can be a barrier for mid-sized companies or those looking for a quick, low-cost pilot.
The Human Element: Developer and Agent Experience
While architecture and ROI are important, the long-term success of an AI platform often depends on the people using it daily. The "Developer Experience" (DX) determines how fast a team can innovate, while the "Agent Experience" (AX) dictates how effectively human employees can collaborate with their AI counterparts. Both Cognigy and Kore.ai have distinct philosophies regarding usability.
Developer Experience: Speed vs. Granularity
Cognigy’s AI Agent Studio is widely praised for its approachability. It is designed to lower the barrier to entry, allowing conversation designers and non-technical business analysts to contribute without constantly relying on IT.
- Visual Intuition: The flow builder uses a clean, logic-based visual interface. Complex processes are represented as easily readable charts. This visualization helps teams quickly identify bottlenecks in a conversation without parsing through lines of code.
- Collaborative Design: The 2025 updates brought real-time multi-user editing, similar to working in a shared document. This feature is a major benefit for agile teams where a copywriter might tweak the tone of a response while a developer configures the API connection for the same node simultaneously.
- Testing and Debugging: Cognigy offers an "Interaction Panel" that sits alongside the flow builder. It allows developers to test the bot’s logic step-by-step in real-time, providing immediate feedback on variable states and API calls.
Kore.ai's XO Platform offers a more dense, feature-rich environment. It is built for "Power Users" who require granular control over every aspect of the interaction.
- Complexity for Power: The interface is packed with options. While this presents a steeper learning curve, it offers unmatched control for developers who need to script complex behaviors. The platform supports "Digression Management" settings at a very granular level, allowing fine-tuning of how and when a bot should switch topics.
- Unified Flow Builder: The recent convergence of voice and digital flows into a single builder has streamlined the experience, but the sheer number of configuration options (channels, languages, authentication, varying responses) can be overwhelming for smaller teams.
- Versioning and Lifecycle: Kore.ai shines in its rigorous approach to lifecycle management. Its built-in tools for version control, publishing, and rollback are reminiscent of traditional software development environments, which appeals heavily to enterprise IT departments.
The Agent Experience: AI as a Copilot
In 2026, the goal is not just to replace humans but to augment them. Both platforms offer "Copilot" or "Assist" technologies that sit on the human agent's desktop, listening to calls and reading chats to provide real-time support.
Cognigy Agent Copilot is tightly integrated with the Contact Center (CCaaS). As a live agent speaks with a customer, the AI listens and instantly retrieves relevant knowledge base articles, suggests next best actions, and even drafts responses. Its primary benefit is reducing "Average Handle Time" (AHT) in high-pressure voice environments. It can also automatically summarize a voice call and update the CRM immediately after the call ends, saving the agent minutes of wrap-up work.
Kore.ai AgentAssist approaches assistance from a broader workflow perspective. It not only suggests answers but can also execute tasks on behalf of the agent. It excels in complex troubleshooting scenarios. If a bank agent is helping a client with a loan, the AgentAssist can pull up current rates, calculate monthly payments, and generate the application form in the background. It also includes strong "coaching" features, analyzing the sentiment of the call in real-time and alerting the agent if they are speaking too fast or if the customer is becoming agitated.
Executive Summary: The Final Verdict
As we look toward 2026, the distinction between Cognigy and Kore.ai becomes clear. It is no longer a question of "which is better," but "which fits our operational DNA?"
| Feature | Cognigy.AI | Kore.ai |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | High-Volume Customer Service (B2C) | Enterprise-Wide Automation (B2B/B2E) |
| Primary Strength | Voice Latency & Contact Center Integration | Multi-Agent Orchestration & Workflow |
| User Base | Customer Service Leaders (CX) | CIOs & IT Transformation Leaders |
| Deployment Speed | Fast (Low-Code/No-Code focus) | Moderate (Requires configuration) |
| Voice Capability | Native, Low-Latency (~500ms) | Capable, Higher Latency (~800ms) |
| 2026 Outlook | Deep integration with NICE CXone | Expansion into global cloud partnerships |
Cognigy is the specialist. It is the scalpel—precise, fast, and incredibly effective for the specific surgery of customer interaction. If your organization lives and dies by the quality of its customer support, specifically in voice, Cognigy is the superior choice.
Kore.ai is the generalist. It is the Swiss Army knife—robust, versatile, and capable of solving problems across every department. If your goal is to build a unified "AI Mesh" that serves employees, partners, and customers through a single, governed infrastructure, Kore.ai provides the necessary breadth.
The "winner" for 2026 is the platform that aligns with your specific bottleneck: Conversation (Cognigy) or Process (Kore.ai).
Ready to Get Started?
14-day free trial
Stay Updated
Related Articles
DOM Downsampling for LLM-Based Web Agents
We propose D2Snap – a first-of-its-kind downsampling algorithm for DOMs. D2Snap can be used as a pre-processing technique for DOM snapshots to optimise web agency context quality and token costs.
A Gentle Introduction to AI Agents for the Web
LLMs only recently enabled serviceable web agents: autonomous systems that browse web on behalf of a human. Get started with fundamental methodology, key design challenges, and technological opportunities.
